Process Overview
Adopting the latest Technology for Efficient and Reliable Manufacturing
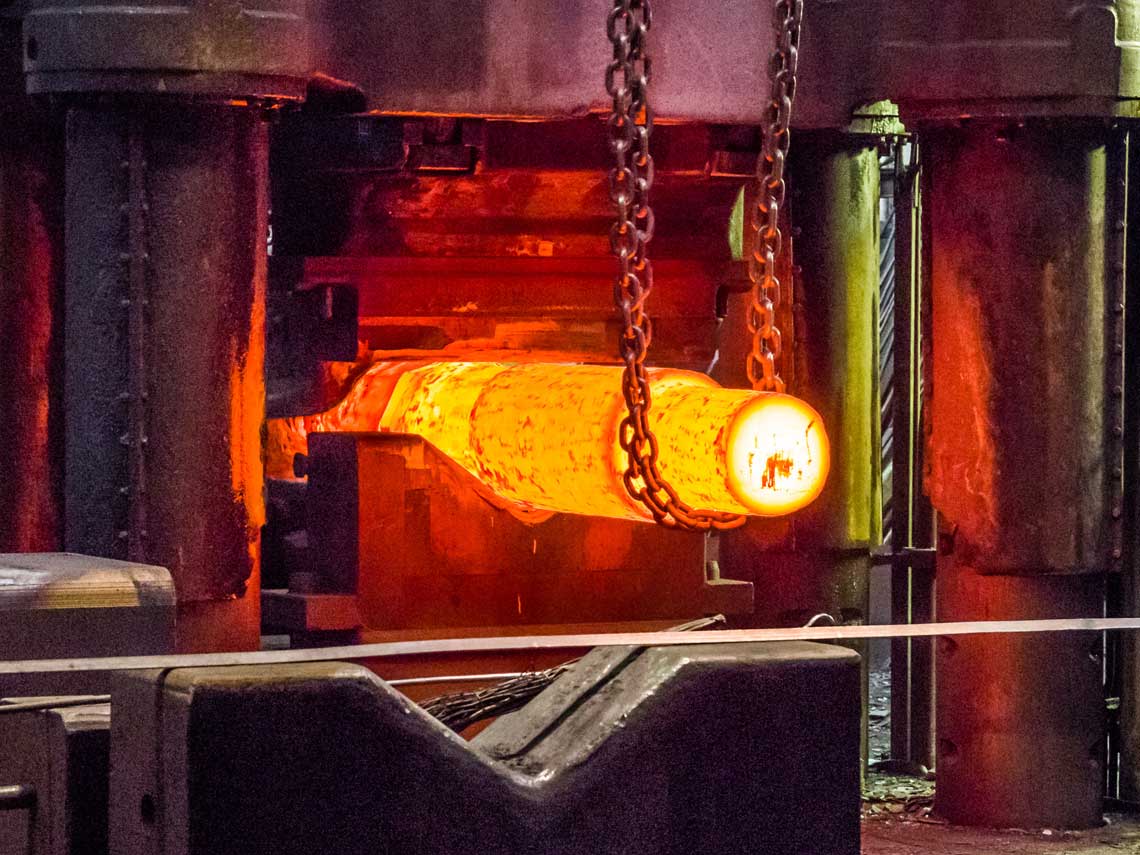
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces of a hammer or a die (Open Die & Closed Die). Forgings are broadly classified based on the temperature at which it is formed as Cold, Warm & Hot forging. For the latter two, the material is heated up to a certain range of temperature. Depending on the type of die used the Closed die shall provide better dimensional control and strength. To meet the increasing demand for customized part requirements many new forging technologies have evolved such :
It is used to produce seamless rings varying in size from a few inches in diameter and weighing less than a pound to over 20 feet in diameter.
Part is forged with the help of four dies arranged in one plane acting simultaneously in radial direction.
Part is held in a die cavity and forged by compressive forces of the upper die revolving on an inclined axis.
It involves locally heating a metal bar and then, while holding it firmly with special tooling, applying pressure to the end of the bar in the direction of its axis to deform it.
It is done by deforming metal and flowing it into a chamber, and then compressing the metal while it is inside the chamber at extreme temperatures.
Materials
Commodities that we emulsify into Finished product
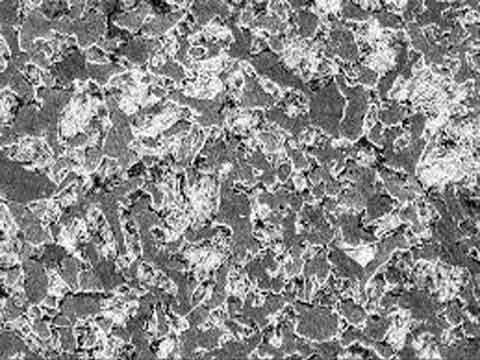
Carbon Steels

Low Alloy Steels
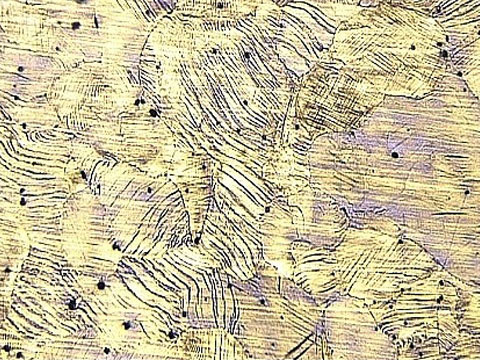
High Alloy Steels
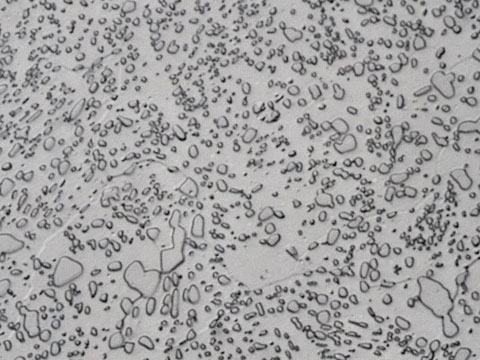
Tool Steels

Non-Ferrous Alloys
Nickel-Cobalt based Alloys
Capabilities
A synopsis of our Skills and Expertise
- Prototype to high volume production of up to thousands of parts per year based on part configuration.
- Forging of parts from few Kgs up to more than 10 Tonnes.
- Manufacturing of wide variety of material grades such as Carbon steel, Alloy steel, Tool steel and Superalloys.
- Gas and Electric operated Heat Treatment furnaces for heating of pre-form as well post heat treatment such as Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, Tempering etc.
- Up to 4000 Tonnes fully automatic Hydraulic press.
- Mobile charging machines and forging manipulators.
- Flexibility of end-to-end machining of small to large sized parts.
- Tolerance of close die forged parts up to ± 0.25mm based on the characteristics of the part and machined tolerance of up to ± 0.02mm.
- CMM inspection for part validation and approval of machined parts.
- In-house lab tests carried out for raw material verification at production site, certified to NABL standards.
- Complete NDT testing of parts for defect analysis as per international standards.
- Manufacturing facility certified to IATF 16949 and AS 9100 Rev.D Quality Management System.
- Globally approved system, client, and product certifications.
Application and Benefits
Gain an Advantage over your Competition



- A variety of forged parts are used in the Aerospace and Defence industry specifically made from Aluminum alloys, Alloy steels, Superalloys and composites. Few of them are shafts, turbine blades, torpedo’s, canisters, domes, missile launchers etc.
- Common applications in Oil & Gas, Valve and Power Generation sector include flanges such as weld-neck, rolled, lap-joint flange; rings and connectors such as seat ring, labyrinth ring, seal ring retainer ring, body adapter etc.
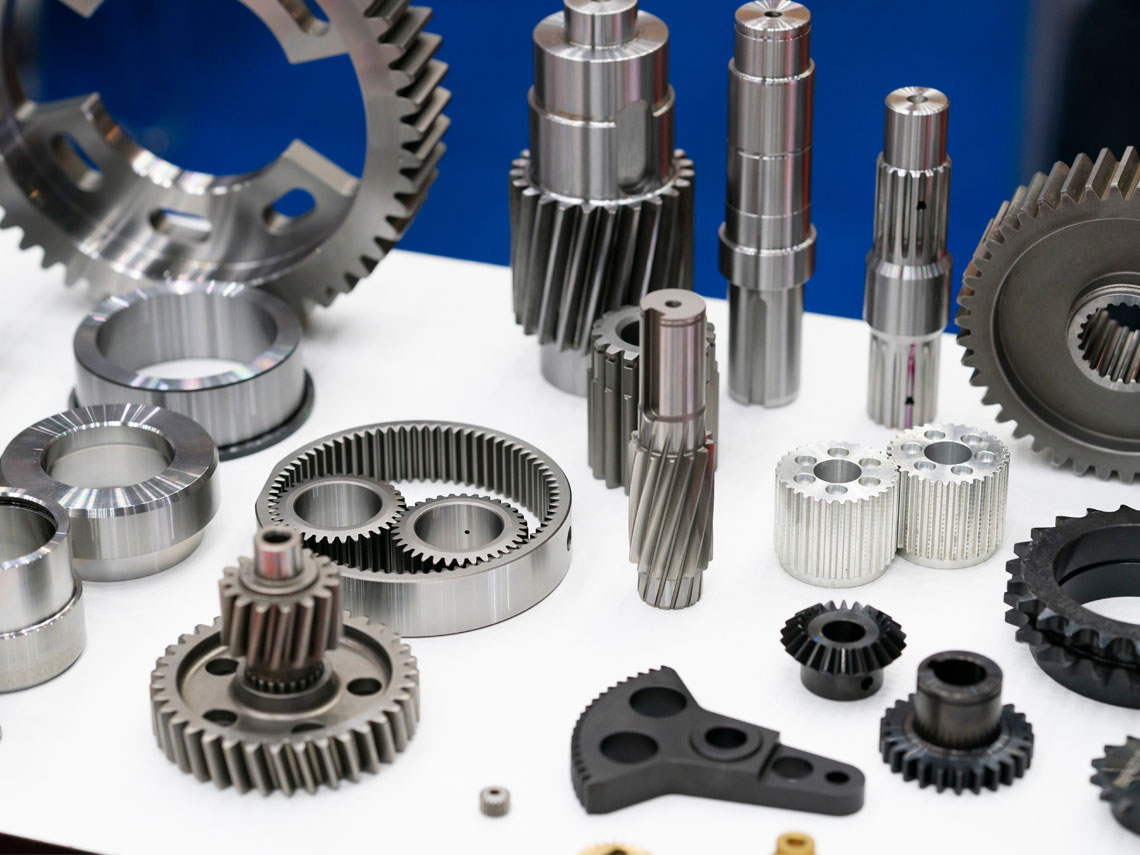
- Other general engineering applications include shafts, gears, pistons and cylinders, transmission parts etc.
-
Forgings are used particularly in critical applications where the parts are subjected to extreme operating environment. Few of their benefits over castings are listed below :
- Higher strength, toughness, and structural integrity
- Longer service life
- Higher design stresses
- Increased safety due to ductility
- Greater strength to weigh ratio
- No porosity
Frequently Asked Questions
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
- It is a manufacturing process which involves shaping of metal through hammering, pressing, or rolling. It can be broadly classified as Open die and Closed die forging.
- The various types of forging process that we can undertake for your parts are ring rolling, radial forging, orbital forging, upset forging, extrusion forging etc. For more details, please refer the Overview section of this page.
- Forged parts have higher strength and toughness and is less susceptible to cracking and shearing under compressive load. Forgings have minimal defects which can be refined by pre-working.
- They have a better response to heat treatment and have a lower cost over component life.
- Castings are preferred to make more complex shaped parts with varying thickness.
- Forged parts are commonly found at point of stress and shock. Automotives such as cars and trucks consist of more than 250 forged parts most of which are produced from carbon or alloy steel. Few of the parts include connecting rods, crankshafts, gear and pinion, universal joints, rocker arms etc.
- Other industries which require forgings include Aerospace and Defence, Oil & Gas, Steel, Valves etc.
-
There can be multiple imperfections in a forging which if present prominently can be termed as a defect. Few of them are :
- Unfilled section – Some part of the forging section remains unfilled.
- Cold shut – It includes small cracks at the corners.
- Scale pits – Due to improper cleaning of forged surface.
- Die shift – Due to misalignment of upper and lower die.
- Residual stress and Flakes – Due to improper cooling of forge product.
- Surface cracking – Due to excessive working on surface at low temperature.
- Chemical analysis – To ascertain the chemistry of the material usually done by spectrometry.
- Mechanical testing – To verify the mechanical properties such as strength, hardness, and ductility. Various tests performed include hardness test, tensile test, bend test, fracture toughness, fatigue test etc.
- NDT – To verify any surface or internal defects in forging. We perform Ultrasonic, Radiography, Magnetic particle, and Liquid penetrant test.
- Metallurgical test – To evaluate the physical characteristics of the forged material and check for any defects. This includes microstructure, macrostructure, and grain size.
- We have developed and keep upgrading our capabilities by adding professional and experienced vetted suppliers to our vendor network. Please refer to Capability section of this page for more details.